Overview
Fiscal policy can be used to correct demand-pull inflation.
Fiscal policy is the means by which a government adjusts its spending levels and tax rates to monitor and influence a nation's economy.
Demand-pull inflation occurs when prices are pulled up by increases in aggregate demand that are not matched by equivalent increases in aggregate supply.
Deflationary fiscal policy
Deflationary fiscal policy can be implemented by
Increasing income tax
Cutting government spending.
Higher-income tax reduces disposable income and therefore reduces consumer spending. That also happens when the government cuts subsidies or transfer payments including welfare programs.
Effectiveness of fiscal policy to reduce inflation.
Raising income tax to reduce demand-pull inflation may backfire.
This is because workers may seek higher wages to maintain their disposable income. If their wage claims are granted, firms’ costs of production may increase. Higher costs can generate cost-push inflation.
Higher income tax rates may create disincentive effects.
Some workers may respond to a reduction in disposable income by leaving the labour force. This will reduce the economy’s productive capacity and so reduce aggregate supply.
Monetary policy can be used to reduce demand-pull inflation.
Monetary policy involves altering the supply of money in the economy or manipulating the rate of interest.
Target inflation rate
Central banks have a target rate for inflation and are instructed to use interest rate changes to achieve it. If the inflation rate is rising outside its target range, a central bank is likely to raise the rate of interest.
Raising interest rates to tackle demand-pull inflation
If inflation is forecast to be excessive, increasing interest rates should increase saving, reduce borrowing and reduce investment, thus reducing aggregate demand in the economy. With lower aggregate demand, there is less pressure for suppliers to increase prices as they struggle to hit sales targets, so inflationary pressure is reduced.
Effectiveness of monetary policy to tackle inflation.
A rise in the rate of interest may not always discourage consumer expenditure.
Commercial banks usually do keep their interest rates in line with the central bank’s as it is the rate they will have to pay if they need to borrow from the central bank. There is, however, no guarantee that they will always raise their interest rates when the central bank increases its rate. Furthermore, even if consumers are faced with higher interest rates, they may not reduce their spending if they are optimistic about the future.
There may be time lags.
It can take up to 18 months for interest rate increases to reduce spending.
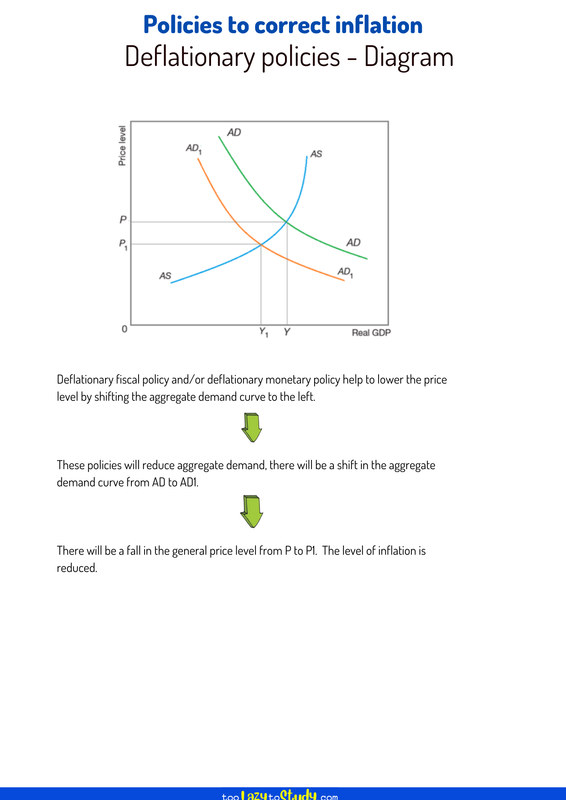
Deflationary fiscal policy and/or deflationary monetary policy help to lower the price level by shifting the aggregate demand curve to the left.
These policies will reduce aggregate demand, there will be a shift in the aggregate demand curve from AD to AD1.
There will be a fall in the general price level from P to P1. The level of inflation is reduced.
.png)
Economics notes on
Deflationary policies - Diagram
Perfect for A level, GCSEs and O levels!