top of page
Overview
Economies of scale
Spreading fixed costs over a larger amount of output is one of the most important sources of economies of scale, the tendency for the cost per unit to fall as output rises.
For example, a full lorry does not cost much more to run than a half-full one, but the full one's costs are spread across twice the amount of goods. Management costs, and those of advertising, are similarly spread over a larger amount of output.
Diseconomies of scale
Diseconomies of scale, in other words rising unit costs, also apply after a certain point.
For example, there is the tendency, above a certain size of company, for lean and efficient management to be replaced by layers of bureaucracy.
.png)
Economics notes on
Marginal cost and average costs
Perfect for A level, GCSEs and O levels!
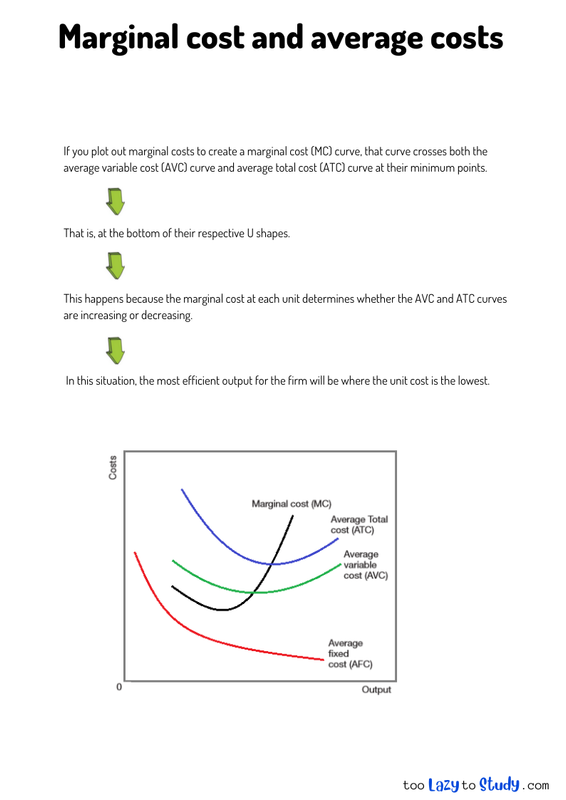

bottom of page
