top of page
Overview
Interaction of demand and supply– markets in equilibrium
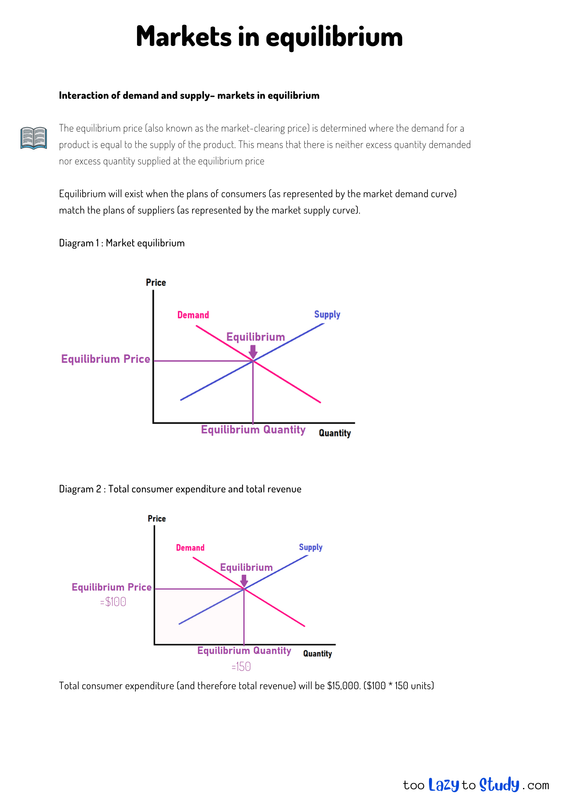
The equilibrium price (also known as the market-clearing price) is determined where the demand for a product is equal to the supply of the product. This means that there is neither excess quantity demanded nor excess quantity supplied at the equilibrium price
Equilibrium will exist when the plans of consumers (as represented by the market demand curve) match the plans of suppliers (as represented by the market supply curve).
Diagram 1 : Market equilibrium
Diagram 2 : Total consumer expenditure and total revenue
Total consumer expenditure (and therefore total revenue) will be $15,000. ($100 * 150 units)
.png)
Economics notes on
Markets in equilibrium
Perfect for A level, GCSEs and O levels!

bottom of page
