Overview
Positive production externalities
Positive production externalities are benefits to third parties and are created by producers of goods and services.
If a forestry company plants new woodlands, there is a benefit not only to the company itself but also to the world through a reduction of CO2 in the atmosphere (forests are a carbon sink). The marginal social cost of providing timber, therefore, is less than the marginal private cost.
Diagram explained
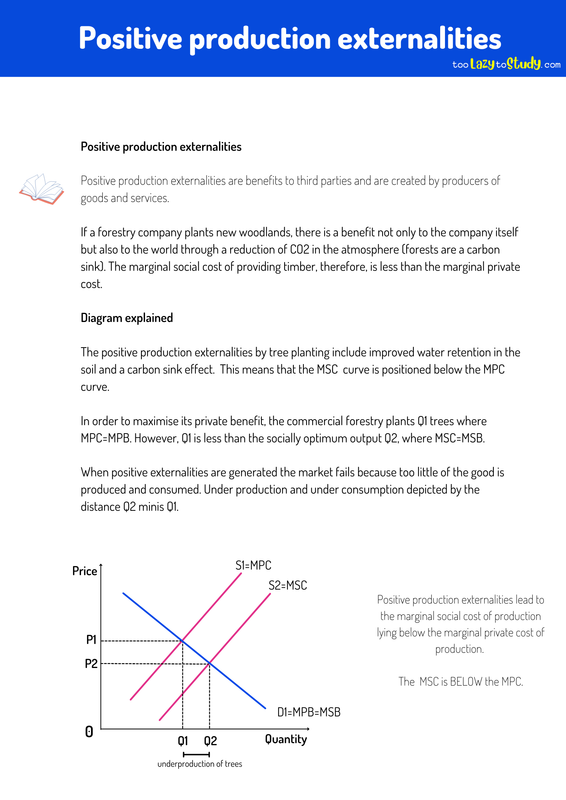
The positive production externalities by tree planting include improved water retention in the soil and a carbon sink effect. This means that the MSC curve is positioned below the MPC curve.
In order to maximise its private benefit, the commercial forestry plants Q1 trees where MPC=MPB. However, Q1 is less than the socially optimum output Q2, where MSC=MSB.
When positive externalities are generated the market fails because too little of the good is produced and consumed. Under production and under consumption depicted by the distance Q2 minis Q1.
.png)
Economics notes on
Positive production externalities
Perfect for A level, GCSEs and O levels!