Economics explained
Category:
Market failure
Demerit goods- Negative consumption externalities
The secret to scoring awesome grades in economics is to have corresponding awesome notes.
A common pitfall for students is to lose themselves in a sea of notes: personal notes, teacher notes, online notes textbooks, etc... This happens when one has too many sources to revise from! Why not solve this problem by having one reliable source of notes? This is where we can help.
What makes TooLazyToStudy notes different?
Our notes:
-
are clear and concise and relevant
-
is set in an engaging template to facilitate memorisation
-
cover all the important topics in the O level, AS level and A level syllabus
-
are editable, feel free to make additions or to rephrase sentences in your own words!
Looking for live explanations of these notes? Enrol now for FREE tuition!
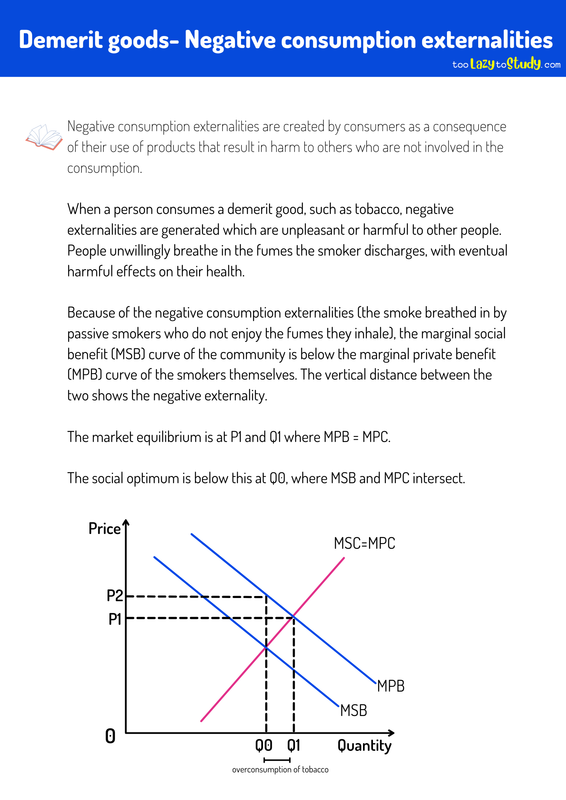
Negative consumption externalities are created by consumers as a consequence of their use of products that result in harm to others who are not involved in the consumption.
When a person consumes a demerit good, such as tobacco, negative externalities are generated which are unpleasant or harmful to other people.
People unwillingly breathe in the fumes the smoker discharges, with eventual harmful effects on their health.
Because of the negative consumption externalities (the smoke breathed in by passive smokers who do not enjoy the fumes they inhale), the marginal social benefit (MSB) curve of the community is below the marginal private benefit (MPB) curve of the smokers themselves. The vertical distance between the two shows the negative externality.
The market equilibrium is at P1 and Q1 where MPB = MPC.
The social optimum is below this at Q0, where MSB and MPC intersect.