top of page
Economics explained
Category:
Demand and supply
Markets in equilibrium
The secret to scoring awesome grades in economics is to have corresponding awesome notes.
A common pitfall for students is to lose themselves in a sea of notes: personal notes, teacher notes, online notes textbooks, etc... This happens when one has too many sources to revise from! Why not solve this problem by having one reliable source of notes? This is where we can help.
What makes TooLazyToStudy notes different?
Our notes:
-
are clear and concise and relevant
-
is set in an engaging template to facilitate memorisation
-
cover all the important topics in the O level, AS level and A level syllabus
-
are editable, feel free to make additions or to rephrase sentences in your own words!
Looking for live explanations of these notes? Enrol now for FREE tuition!
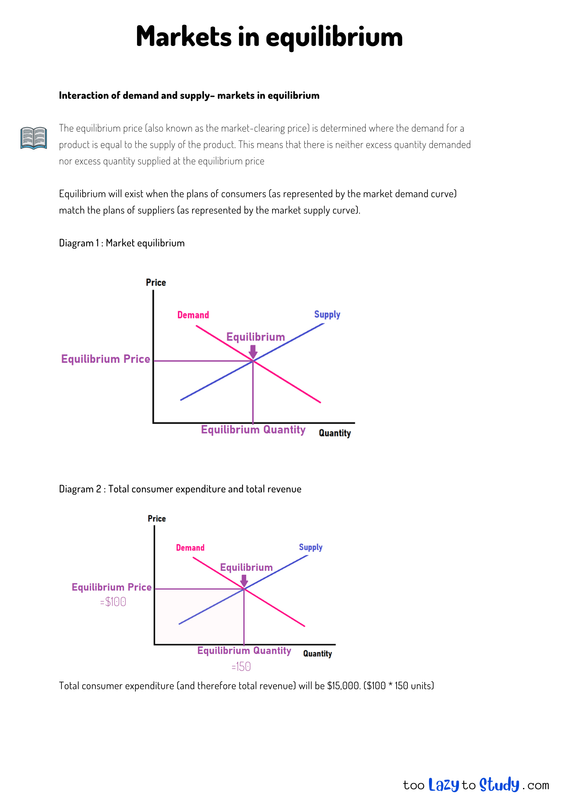
Interaction of demand and supply– markets in equilibrium
The equilibrium price (also known as the market-clearing price) is determined where the demand for a product is equal to the supply of the product. This means that there is neither excess quantity demanded nor excess quantity supplied at the equilibrium price
Equilibrium will exist when the plans of consumers (as represented by the market demand curve) match the plans of suppliers (as represented by the market supply curve).
Diagram 1 : Market equilibrium
Diagram 2 : Total consumer expenditure and total revenue
Total consumer expenditure (and therefore total revenue) will be $15,000. ($100 * 150 units)
bottom of page