Economics explained
Category:
Market structures
Perfect competition - Long run
The secret to scoring awesome grades in economics is to have corresponding awesome notes.
A common pitfall for students is to lose themselves in a sea of notes: personal notes, teacher notes, online notes textbooks, etc... This happens when one has too many sources to revise from! Why not solve this problem by having one reliable source of notes? This is where we can help.
What makes TooLazyToStudy notes different?
Our notes:
-
are clear and concise and relevant
-
is set in an engaging template to facilitate memorisation
-
cover all the important topics in the O level, AS level and A level syllabus
-
are editable, feel free to make additions or to rephrase sentences in your own words!
Looking for live explanations of these notes? Enrol now for FREE tuition!
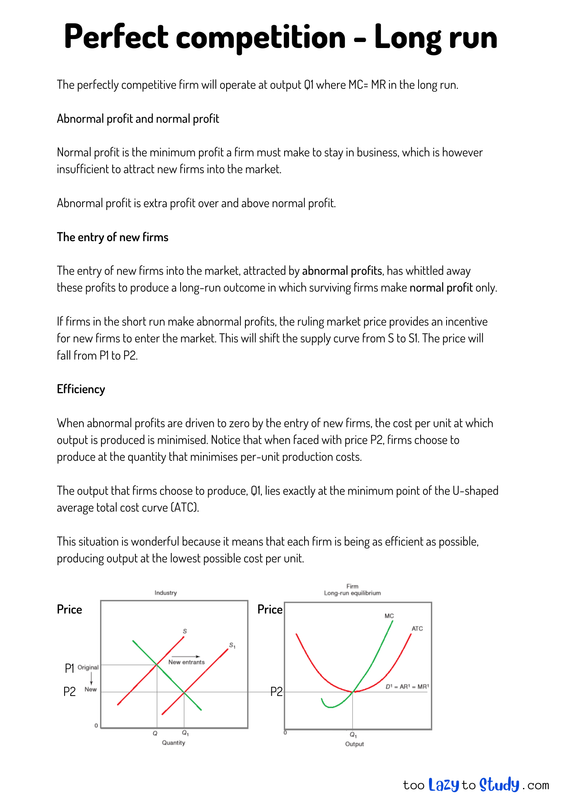
The perfectly competitive firm will operate at output Q1 where MC= MR in the long run.
Abnormal profit and normal profit
Normal profit is the minimum profit a firm must make to stay in business, which is however insufficient to attract new firms into the market.
Abnormal profit is extra profit over and above normal profit.
The entry of new firms
The entry of new firms into the market, attracted by abnormal profits, has whittled away these profits to produce a long-run outcome in which surviving firms make normal profit only.
If firms in the short run make abnormal profits, the ruling market price provides an incentive for new firms to enter the market. This will shift the supply curve from S to S1. The price will fall from P1 to P2.
Efficiency
When abnormal profits are driven to zero by the entry of new firms, the cost per unit at which output is produced is minimised. Notice that when faced with price P2, firms choose to produce at the quantity that minimises per-unit production costs.
The output that firms choose to produce, Q1, lies exactly at the minimum point of the U-shaped average total cost curve (ATC).
This situation is wonderful because it means that each firm is being as efficient as possible, producing output at the lowest possible cost per unit.