top of page
Economics explained
Category:
Exchange rates
The J curve effect
The secret to scoring awesome grades in economics is to have corresponding awesome notes.
A common pitfall for students is to lose themselves in a sea of notes: personal notes, teacher notes, online notes textbooks, etc... This happens when one has too many sources to revise from! Why not solve this problem by having one reliable source of notes? This is where we can help.
What makes TooLazyToStudy notes different?
Our notes:
-
are clear and concise and relevant
-
is set in an engaging template to facilitate memorisation
-
cover all the important topics in the O level, AS level and A level syllabus
-
are editable, feel free to make additions or to rephrase sentences in your own words!
Looking for live explanations of these notes? Enrol now for FREE tuition!
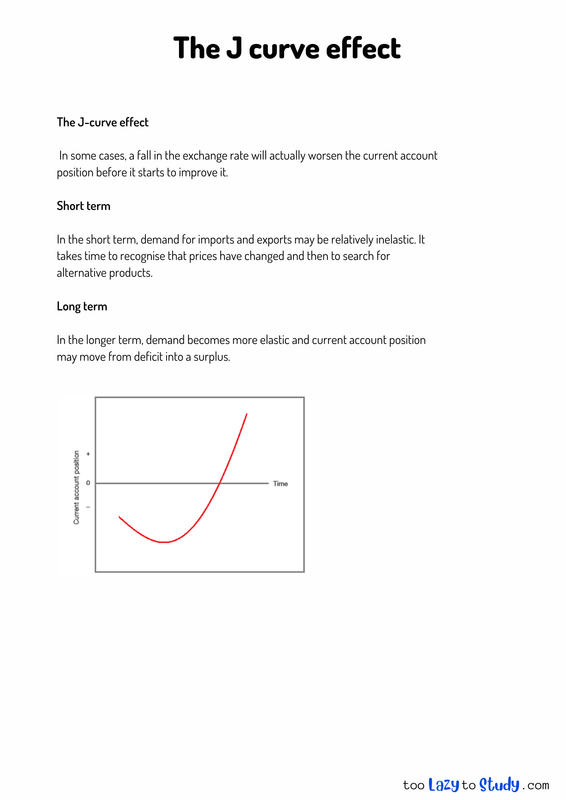
The J-curve effect
In some cases, a fall in the exchange rate will actually worsen the current account position before it starts to improve it.
Short term
In the short term, demand for imports and exports may be relatively inelastic. It takes time to recognise that prices have changed and then to search for alternative products.
Long term
In the longer term, demand becomes more elastic and current account position may move from deficit into a surplus.
bottom of page